What You Need to Know
About Ecommerce Security
How can modern ecommerce and online businesses efficiently prevent costly data breaches and
avoid harsh legal sanctions by implementing well-though cybersecurity, data protection
and privacy? Let’s explore emerging digital risks and antihacking strategies.
$15.1 Billion
logins and passwords stolen
during 2019
$149,000
is the average cost of a data
breach for SMB in 2019
90%
of web & mobile apps have
high-risk security flaws
76%
of SMEs in the US say they
were hacked in 2019
200 days
is the average data breach
detection timeframe
Statistics for 2020 by Varonis
Ecommerce Security and Data Breaches
Nowadays, virtually all industries have a swiftly increasing Internet presence, providing their customers and partners with an instant service around the clock, agile workflow and simple online payment. The growing range of enterprises entering into the emerging space of ecommerce spans from traditional and conservative businesses to highly disruptive startups mastering AI and blockchain.

The most popular market segments that adopt online business and shift to ecommerce include:
- accounting
- retail and grocery shops
- online and mobile payments
- healthcare providers and telemedicine
- insurance and brokerage companies
- restaurants and food delivery
- travel and hotel booking
- taxi and car sharing
- media and games
- legal services
- public sector
- real estate
They all have a wide spectrum of fairly different cyber risks and digital threats, nonetheless, having one certain thing in common: being a highly attractive target for mushrooming groups of sophisticated cybercriminals. The more Internet presence organizations have, the bigger is their external attack surface is, enabling additional attack vectors and hacking techniques against the organization.
Want to have an in-depth understanding of all modern aspects of Cybersecurity of Digital Transformation for Online Business and e-Commerce? Read carefully this article and bookmark it to get back later, we regularly update this page.
Most of the victims active in the ecommerce and online business, however, don’t perceive or largely underestimate these risks, frankly believing that the size or the nature of their business makes them unattractive for skilled hackers, granting them with a digital immunity. Regrettably, this widespread belief is fatally incorrect and has already driven many promising companies out of their business or wiped out years of profitability in a best-case scenario.
Frequently, shrewd cybercriminals avoid attacking their victims directly, but rather targeting partners and other trusted third parties of the desired victim who have privileged access to the documents or data chased by the attackers. The more customers of an important size you have, the more chances you get that professional hackers will pick you up as their target.
Experienced cybercriminals virtually never attack large organizations or companies frontally, instead going after their suppliers and services providers including IT vendors, accountants or law firms. In light of a comparatively weaker cyber defense and oftentimes deficient security controls, this indirect approach significantly reduces the costs and complexity of an intrusion, makes incident detection and investigation highly unlikable and thus wisely exonerates the attackers from being detected and prosecuted by law enforcement agencies. Sometimes, even if the breach is later detected, smaller victims have no financial capacity to properly investigate and otherwise respond to it. While the attackers will get exactly what they are looking for without hacking the primary target directly. Hence, companies of all sizes coming from any industry segment are inevitably on the omniscient radar of unscrupulous cybercriminals.
Additionally, careless SMEs are almost inevitably falling victims to well-organized cyber gangs focused on wide-scale and low-complexity hacking campaigns. This includes automated exploitation of publicly known vulnerabilities in outdated WordPress or Magento web software. Cyber gangsters are continuously monitoring the Internet by using Shodan or special Google dorks, looking for exposed and vulnerable applications, servers and websites. Once a susceptible target is spotted, it’s automatically hacked, backdoored and even patched to preclude rival gangs from getting in later. Once attackers gather a few hundreds of Trojan’ed systems or websites, they sell them as a bundle on Dark Web marketplaces for as low as from $1 to $10 per compromised system. Afterwards, the systems are used to send spam, host pornography, conduct DDoS attacks or even launch sophisticated intrusions into governmental systems perfidiously camouflaging real identity of the attackers. Later, unwitting SMEs may get raided by law enforcement agents and even get indicted with a grim gamut of criminal charges for unlawful hacking or theft of intellectual property.
Free DemoEcommerce Compliance and Data Protection Regulations

Companies of all sizes have to comply with the data protection enacted laws and imposed privacy regulations in e-commerce, online business and digital space. Perhaps, EU’s GDPR is the most widely known one thanks to severe financial penalties for non-compliance that may attain as much 4% of the yearly turnover or 20 million Euros, whatever is greater. This European law enacted in 2016 and fully enforceable from 2018 applies to all companies that process or store Personally Identifiable Information (PII) of European residents. Even a minor failure may trigger a complaint to a data protection authority, investigation and a penalty. Recently, the state of California enacted a similar state law CCPA purported to safeguard PII of Californians.
All businesses that process credit card transactions, regardless of volume of such transactions, are required to comply with PCI DSS under a penalty of fine and immediate suspension of authorization to process any credit card transactions, such as Visa, Master Card or American Express.
These are just a few laws and regulations to name amid the growing complexity of a modern-day compliance landscape. Furthermore, an unprecedently high number of businesses across the globe face an incremental number of incoming requests from their customers to provide a convincing proof of relevant data protection processes such ISO 27001 certification or PCI DSS SAQ (Self-Assessment Questionnaire).
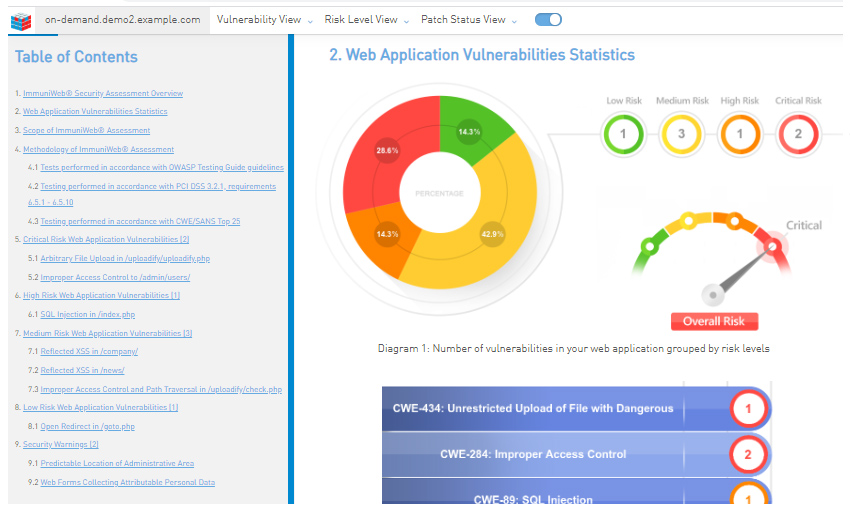
One single XSS or SQL injection vulnerability on a forgotten subdomain, or accidentally exposed cloud storage on Amazon’s public cloud, may lead to a disastrous data breach, and a subsequent loss of business, fines from regulatory watchdogs and civil lawsuits from customers whose data is compromised. Worse, if technical investigation and forensics conducted by law authorities reveals a major non-compliance stemming from negligence or deliberate ignorance (e.g. failure to conduct regular application penetration testing for business-critical systems), European and American courts will likely demonstrate no leniency when imposing monetary fine and concomitant civil penalties.
Free DemoEcommerce Security Risks

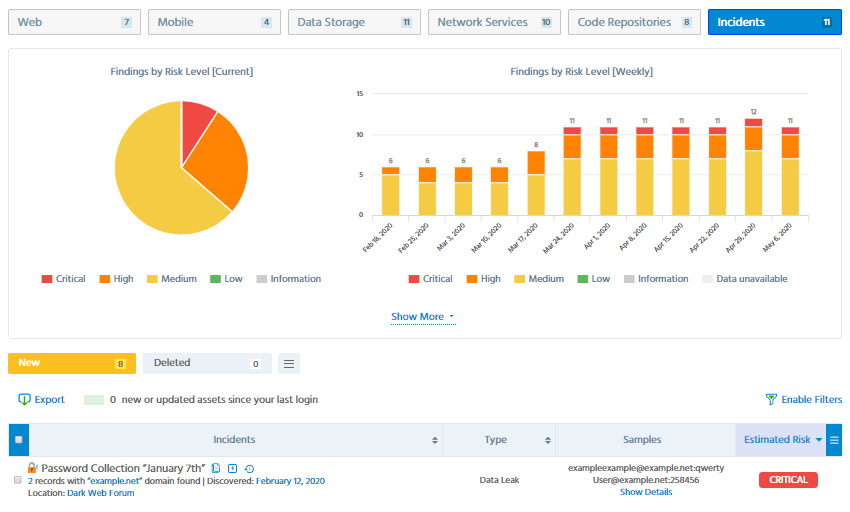
Phishing, ransomware and magecart attacks against ecommerce and online business make spooky headlines every morning. Spanning from comparatively insignificant data leaks impacting a few thousands of individuals to hundreds of millions of hacked accounts with sensitive or payment data.
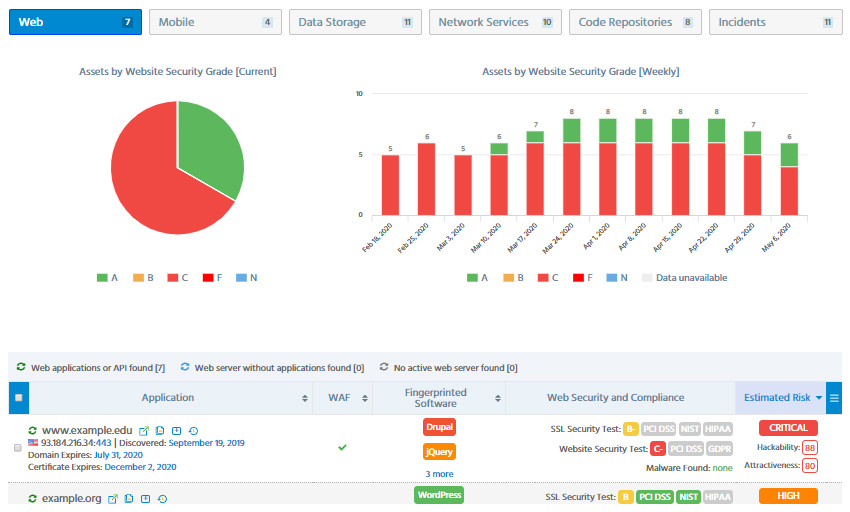
The most prevalent security and privacy issues usually stem from incomplete or outdated visibility of organizational IT assets and data storage. Few organizations maintain a comprehensive inventory of their Internet-facing assets such as websites, APIs, network services or public cloud storage on Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud. Resultingly, these systems are left unmaintained, and as soon as a new security vulnerability comes out, become a widely open door to the organizational crown jewels.
The second common problem is outdated software, being aptly exploited by cybercriminals to get into local networks, databases and file servers. Even one single outdated web CMS can be exploited to compromise web server and potentially the entire network, corporate CRM and ERP.
Third The third most alarming issue likewise figures among the most laborious ones to mitigate: human mistake exacerbated by omnipresent forgetfulness and carelessness. Software developers may accidentally leak sensitive source code with hardcoded logins and passwords on GitHub, a network engineer may forget to properly configure access permissions at AWS S3 bucket with confidential information, or a C-level executive may neglect enterprise password policy and use the same password on his or her personal accounts. Watchful attackers rarely miss such invisible time-bombs, systematically converting them into a valuable loot.
Free DemoEcommerce Security Checklist

To avoid falling a victim to cybercriminals we recommend undertaking the following 5 steps:
- Audit access to your data
Verify who has access to your data, including your employees and trusted third parties. Make sure that the access to your data is provided strictly to those ones who really need it within the scope of their professional duties covered by an enforceable NDA, and only to the degree of access that is required for due performance of such duties. - Ensure visibility of your IT assets
Make sure you have a holistic, up2date and comprehensive inventory of your websites, domain names, cloud storage, APIs and all other systems or applications accessible from the Internet. Maintain an inclusive inventory of your commercial and Open Source Software (OSS) used there to properly react to newly reported vulnerabilities. - Implement a patch management program
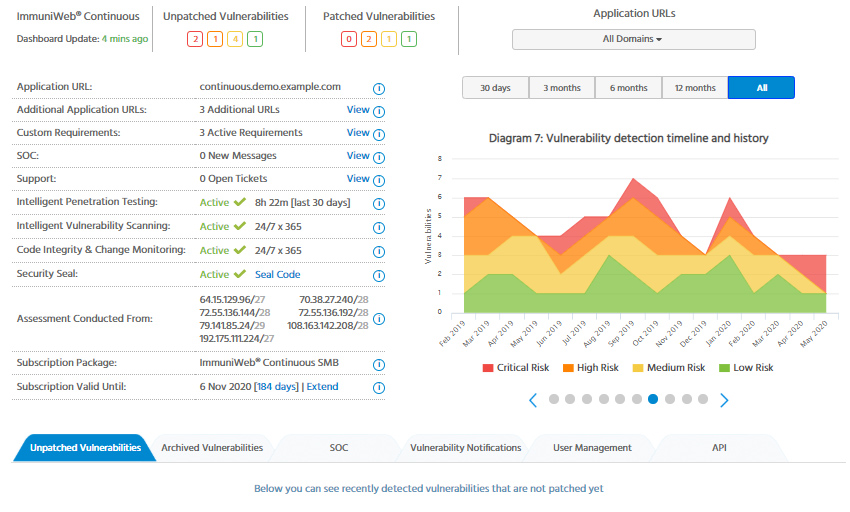
Ascertain that your IT vendors and service providers are capable to rapidly respond to any newly detected vulnerabilities affecting your internal network, home computers, mobile devices and externally exposed infrastructure. Don’t hesitate to ask how frequently they monitor up2dateness of the software, and whether they provide any measurable SLA (Service Layer Agreement) clearly stating how often and how quickly they react to newly reported security flaws affecting your online business. - Secure your web and mobile applications
Vulnerable or unprotected applications is the most frequent intrusion vector in 2020. Double-check how reliable and resilient your applications are, for example by using our free website security test of free mobile app security test. A single web security vulnerability may ruin your previous data protection efforts and let the attackers into your network. - Keep an eye on phishing and squatting
Unscrupulous competitors may bring even more problems than cybercriminals when stealing your customers via cybersquatted and typosquatted domain names. Even more harm is emanated by fake accounts in social networks trying to scam your clientele. At ImmuniWeb, we offer a free online test to detect phishing and squatting in the Internet.
How We Help Prevent Data Breaches and Secure Online Business
- Discover
Your external attack surface
and Dark Web exposure - Prioritize
Your existing risks and threats
in an actionable manner - Audit
Your web and mobile apps
for all known vulnerabilities - Protect
Your infrastructure from
the cyber-attacks and fraud




Informed and Risk-Based Security
Identify, prioritize and mitigate your
cyber risks in a timely manner
Reduced Costs and Complexity
Avoid redundant and overlapping
solutions that you don’t need
Prevented Data Breaches
Ensure holistic visibility and
continuous security monitoring